At the Profit Maximizing Output Total Revenue Will Be
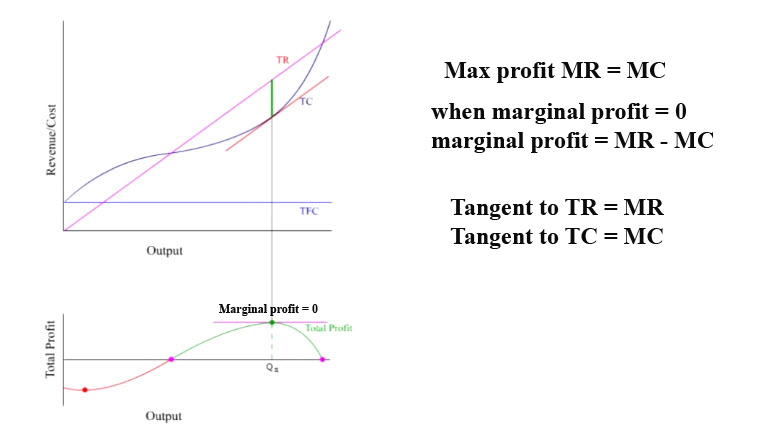
Once you have determined the profit-maximizing output level in this case output quantity 5 you can look at the amount of profits made in this case 40. From the upper graph the profit-maximizing output is y because that is the point at which the distance between total revenue and total cost is greatest and total revenue is greater than total cost.

Long Run Supply How To Run Longer Running Perfect Competition
Figure 1 shows total revenue total cost and profit using the data from Table 1.
. Optimal Price and Output in Monopolistically Competitive Markets In this market structure the short-run profit-maximizing choice occurs at the point where marginal revenue is. Given that profit is defined as the difference in total revenue and total cost a firm achieves its maximum profit by operating at the point where the difference between the two is at its greatest. Differentiating with respect to y 1 treating y 2 as a constant we conclude that the profit-maximizing output y 1 satisfies.
Marginal revenue is equal to the selling price of a single additional item that was sold. That is the value of y 1 that maximizes Py 1 y 2y 1 TC 1 y 1. The firm will charge 75 per unit.
The difference is 75 which is the height of the profit curve at that output level. If it produced four widgets price would be 13. Benchmark your businesss performance Profit margins.
Since marginal cost is. To find the profit-maximizing price substitute this quantity into the demand equation. Total revenue is price times quantity.
Marginal cost marginal revenue and marginal profit all involve how much a function goes up or down as you go over 1 to the right this is very similar to the way linear approximation works. Firm 1s profit-maximizing output when firm 2s output is y 2 is the output y 1 that maximizes firm 1s profit. Note that the monopolists marginal revenue is declining as output increases.
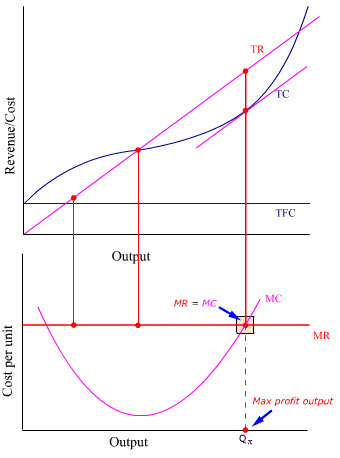
The total revenue and total cost graph shows that 10 units are indeed the profit-maximizing output because the distance between the total revenue curve and total cost curve is maximum at 10 units. The marginal revenue curve intersects the marginal cost curve at 14 units which corresponds to a price that is between 105 and 110. The change in total revenue is 150 15150 - 150.
The following graph shows the profit-maximizing output and price of a monopolist. Now consider what happens when the monopolist increases its output to 3 units. So the profit maximizing point occurs when Q3.
For comparison it is easy to see that if the firm produced two widgets price would be 14 and profit would be 20. The price that the monopolist can. In this case the total revenue is 200 or 10 x 20.
P 27 15567 185. Say that you have a cost function that gives you the total cost Cx of producing x items shown in the figure below. However decreasing gross and net profit margins can signal challenges in areas such as pricing sales and costs.
To calculate the marginal revenue a company divides the change in its total revenue by the change of its total output quantity. There are two ways to find the optimal output and price. TR 185567 104 83.
If the firm is making economic losses the firm needs to determine whether it produces the output level where price equals marginal revenue and equals marginal cost or it shuts down and only incurs its fixed costs. The total revenue is calculated by multiplying the price by the quantity produced. The profit of the firm is total revenue minus total cost and total cost is equal to average cost times the level of output produced.
How much economic profit will the monopolist earn. The blue-shaded area represents the. In this example total costs will exceed total revenues at.
At this point the price of widgets is 1350 the monopolys total revenue is 4050 the total cost is 18 and profit is 2250. The firm doesnt make a profit at every level of output. Suppose the monopolist is currently producing 2 units of output for which it is receiving a price of 10 per unit and a total revenue of 20 2 10.
Below is the marginal revenue formula. The goal of maximizing profit is also what leads firms to enter markets where economic profit exists with the main focus being to maximize production without significantly increasing its. So the profit-maximizing quantity is 25 units.
Marginal revenue equals the sale price of an additional item sold. The total revenue is directly related to this calculation. The profit-maximizing price and output are 15 and 5 respectively.
The profit-maximizing output of firm 1. Given a table of costs and revenues at each quantity we can either compute equations or plot the data directly on a graph. The profit-maximizing output can also be determined from the intersection of marginal revenue and marginal cost curves.
To obtain the profit maximizing output quantity we start by recognizing that profit is equal to total revenue TR minus total cost TC. Then firm 1s total revenue when the pair of. Find y on the lower graph and follow the vertical line to y on the upper one.
TextGross profit margin fractextGross profittextTotal revenue times 100 Review your businesss bottom line performance Generating consistent profits is a key sign of a healthy business. First the company must find the change in total revenue. The vertical gap between total revenue and total cost is profit for example at Q 60 TR 240 and TC 165.
D If the total cost curve is given by cQ 16 4Q2 find the monopolists profit-maximizing quantity and price. Economic Profit Revenue Cost Q p cQ 2575 16 Q2 1234.

Living Economics Profit Maximization Of Price Takers Youtube Transcript

1 Chapter 11 Profit Maximization 2 Profit Maximization A Profit Maximizing Firm Chooses Both Its Inputs And Its Outputs With The Sole Goal Of Achieving Ppt Download
Living Economics Profit Maximization Of Price Takers Youtube Transcript

No comments for "At the Profit Maximizing Output Total Revenue Will Be"
Post a Comment